Patient Information
Biologics
Select from your area of interest below:
Currently viewing: Biologics
When do you need synthetic bone substitute?
You currently suffer from a bone defect that requires a surgical treatment. Bony voids can be surgically created or result from a traumatic injury. The aim of bone grafting surgery is to restore the bone volume, in its shape, width and height.
To that goal, the surgeon will use a bone substitute which is a synthetic product used to fill the defect and to facilitate the bone healing /reconstruction. The Synthetic Bone Substitute is intended for use to reconstruct bony voids or bone gaps of the skeletal system (e.g. extremities, spine and pelvis).
The Synthetic Bone Substitute can be used in adults excluding pregnant women and has not been tested in pediatric population.
The Synthetic Bone Substitute is intended for use by physician familiar with bone void filling and rigid fixation techniques. The Synthetic Bone Substitute is to be handled or implanted by trained qualified physicians having read this instruction for use. The implantation of the device on the patient must be evaluated and confirmed by the physician before surgery, considering the potential contraindications provided from the manufacturer.

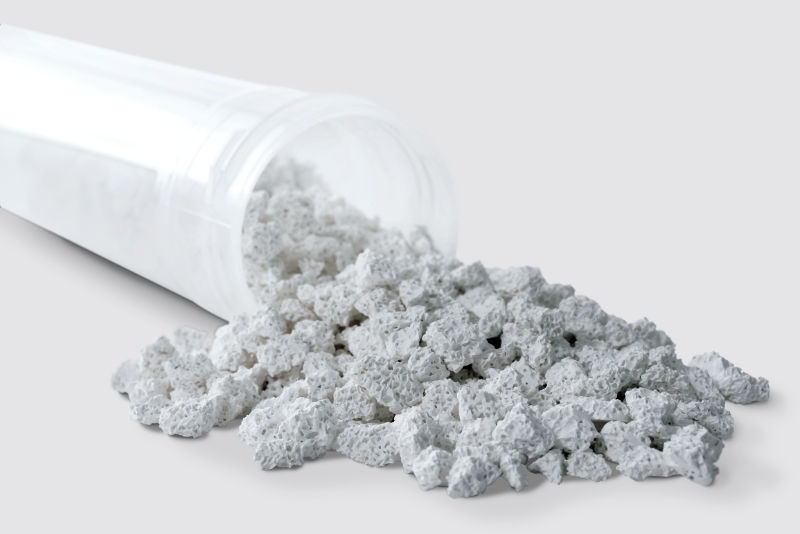
What Is A Synthetic Bone Substitute?
OsteoFlo-G is a bone void filler. This product is a microporous and macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic consisting of 60% Hydroxyapatite (HA) and 40% beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (ß-TCP) particles.
It is a resorbable product which means that it gradually degrades over time and is replaced by new bone. The total resorption of the product depends on numerous factors such as its size and volume, the location of the defect, the surgical technique and the health status of the patient. It is admitted that an optimal bone regeneration is always observed before the complete resorption of the product.
The performances of the device can be affected if the surgery is not performed following standard techniques or if post- operative recommendations given by the physician are not respected.

Adverse events and risks
It is important that patients know about the following possible risks and complications, which include but are not limited to:
- Post-operative discomfort
- Haematoma
- Irritation
- Risk of allergy
- Infection
- Foreign body reaction
- Pain
- Fever
- Inflammatory reaction
- Osmotic shock
- Adverse effects on blood coagulation and blood components
- Thrombosis
- Necrosis
- Non-union/pseudoarthrosis due to displacement product or fibrous encapsulation